Introduction
The grocery store retailing industry is pivotal in the global economy, and customer expenditure on grocery stores is predicted to hit more than $7 trillion by 2025. To retailers, investors, urban planners, and policymakers, determining the Best Grocery Store Location Datasets is imperative to make efficient market entry strategies, enhance regional accessibility, and boost economic development. Precise location information allows stakeholders to Extract Top Grocery Store Locations Data, facilitating more intelligent expansion, competitive, and customer targeting decisions. With technologies that Scrape Grocery Chains Location and Address Data, companies can access real-time, location-based insights regarding store distribution, proximity to customers, and market saturation. Such insights refine retail strategies, increase logistics efficiency, and improve profitability. This publication delves into methods of acquiring quality grocery store location data, sophisticated analytical frameworks for transforming raw data into actionable insights, and the pivotal position such intelligence assumes in defining the grocery retail operations of the future.
Methodologies for Extracting Grocery Store Locations Data
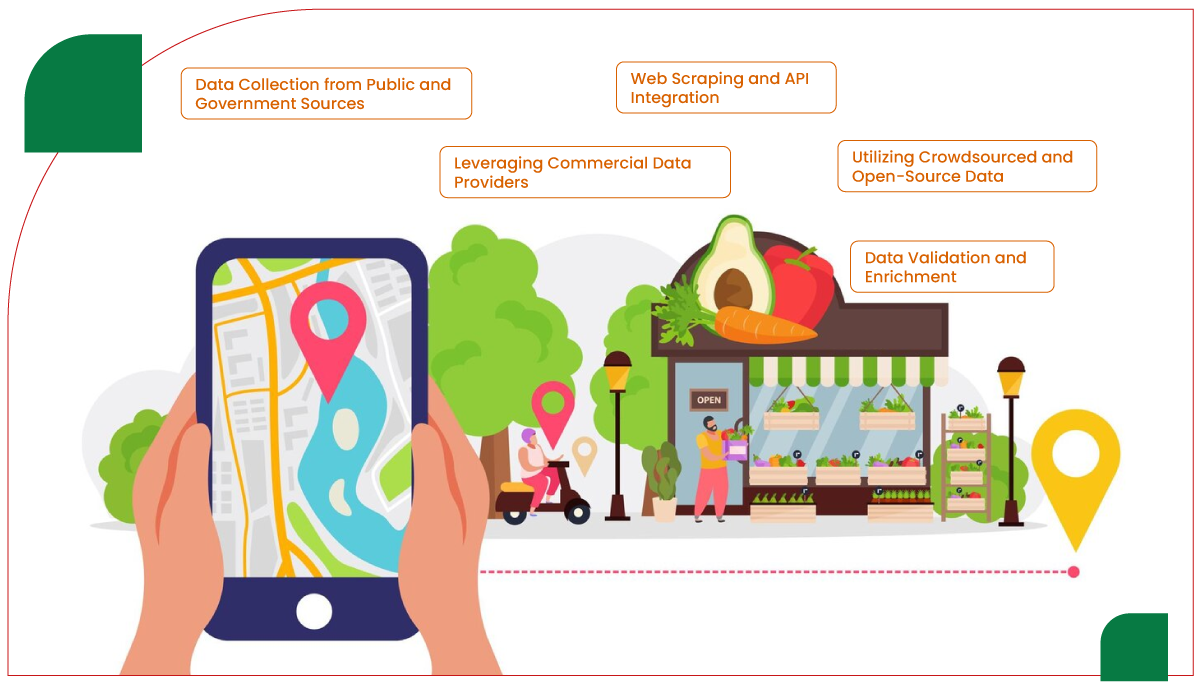
Extracting reliable and comprehensive grocery store location data requires a systematic approach, combining diverse data sources and robust extraction techniques. The following methodologies outline the process of acquiring high-quality data suitable for analysis.
1. Data Collection from Public and Government Sources
Government agencies provide verified datasets that serve as a foundation for location data. For instance, the U.S. Census Bureau’s Business Register and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Environment Atlas offer detailed records of retail establishments, including grocery stores. These datasets include business licenses, zoning details, and economic metrics. Researchers can access these through public portals or Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) requests. The methodology involves:
- Querying databases for retail categories (e.g., NAICS code 4451 for grocery stores).
- Filtering data by geographic region, store type, or operational status.
- Validating records against secondary sources to ensure accuracy. This method is essential for Extracting Best Grocery Store Location Data from reliable sources.
2. Leveraging Commercial Data Providers
Commercial providers like SafeGraph, Nielsen, and Placer.ai offer curated datasets with extensive attributes, such as store coordinates, foot traffic estimates, and demographic profiles. SafeGraph’s Places dataset, for example, includes millions of points of interest (POIs) with metadata specific to grocery stores. The methodology includes:
- Subscribing to provider APIs or purchasing datasets.
- Specifying parameters (e.g., geographic scope, store categories like supermarkets or specialty grocers).
- Integrating data into analytical platforms using formats like CSV or GeoJSON. The Best Grocery Chain Store Location Data Scraper tools often use these services to enhance accuracy and scalability.
3. Web Scraping and API Integration
Online platforms like Google Maps, Yelp, and retailer websites provide real-time location data. APIs like Google Places API enable programmatic access to store details, while web scraping tools (e.g., BeautifulSoup or Scrapy in Python) extract data from unstructured sources. The methodology entails:
- Developing scripts to query APIs or scrape websites for store names, addresses, and coordinates.
- Implementing geocoding to convert addresses into latitude and longitude.
- Cleaning scraped data to remove duplicates or inconsistencies. This cornerstone of Web Scraping Best Supermarket Locations strategies requires high precision and up-to-date inputs.
4. Utilizing Crowdsourced and Open-Source Data
OpenStreetMap (OSM) and similar platforms offer freely accessible geospatial data contributed by global users. These are particularly useful for regions with limited commercial data availability. The methodology involves:
- Querying OSM using tools like Overpass API to extract grocery store POIs.
- Cross-referencing with commercial or government data to verify accuracy.
- Supplementing with user-contributed metadata, such as store hours or categories. Platforms like OSM are ideal for Extracting Store Location Data from Grocery Chains that may not be fully represented in commercial datasets.
5. Data Validation and Enrichment
Validation and enrichment are critical to ensure data quality. This includes:
- Cross-verifying locations across multiple sources (e.g., matching SafeGraph data with Google Maps).
- Enriching datasets with additional attributes, such as store size or customer demographics, using third-party sources like Experian or Esri.
- Standardizing formats (e.g., consistent address structures) for seamless analysis. These techniques help organizations Scrape Best Grocery Store Location Data with increased confidence and granularity.
By combining these methodologies, researchers can construct a comprehensive dataset that balances accuracy, coverage, and depth.
Finding the Best Grocery Store Locations Data
Sourcing high-quality Grocery Store Datasets is the cornerstone of practical market analysis. The best datasets encompass critical attributes: store name, address, geographic coordinates, size, chain affiliation, and operational status. The methodologies above ensure access to reliable sources, but selecting the optimal dataset depends on specific criteria:
- Accuracy: Data must reflect current store statuses, avoiding outdated entries.
- Comprehensiveness: Datasets should cover diverse store types, from supermarkets to discount grocers.
- Geospatial Precision: Exact coordinates enable spatial analysis and mapping.
- Metadata Richness: Attributes like foot traffic, revenue, or local demographics enhance insights and support Grocery Pricing Data Intelligence .
A hybrid approach—combining SafeGraph for primary data, Google Maps API for real-time updates, and OSM for supplementary coverage—yields the most robust dataset. For example, SafeGraph’s dataset might provide core location data, while Google Maps API adds customer ratings, and OSM fills gaps in rural areas.
Analyzing Grocery Store Locations Data
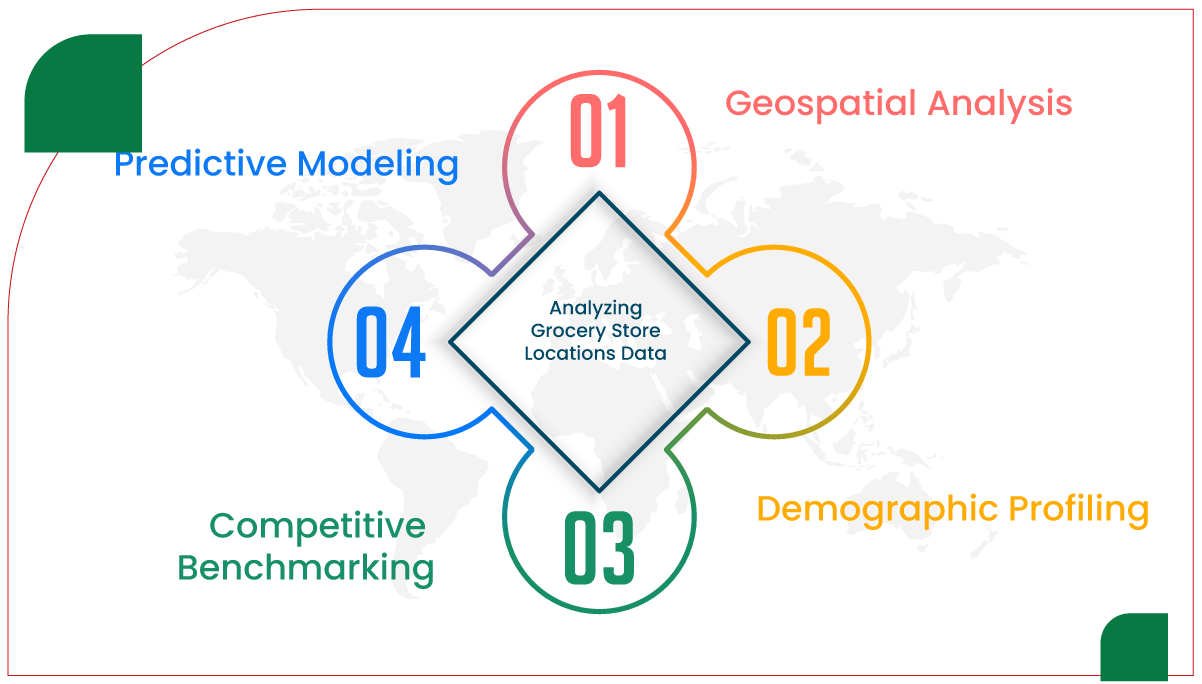
Once collected, grocery store location data must be analyzed to uncover patterns and inform strategies. Analytical approaches include geospatial analysis, demographic profiling, and competitive benchmarking.
1. Geospatial Analysis
Geospatial tools like ArcGIS, QGIS, or Python libraries (e.g., GeoPandas, Folium) map store locations and identify high-performing areas. Key analyses include:
- Heatmapping: Visualizing store density to pinpoint saturated or underserved markets.
- Proximity Analysis: Measuring distances between stores and competitors or population centers.
- Trade Area Analysis: Defining catchment areas based on drive time or population density.
For instance, heat mapping might reveal that urban areas like Chicago have high store density while rural regions lack access, guiding expansion decisions.
2. Demographic Profiling
Linking location data with demographic datasets (e.g., U.S. Census or Esri Tapestry) reveals customer profiles. Analysts can:
- Assess income levels, age groups, or household sizes near stores.
- Identify areas with high demand for specific products (e.g., organic goods in affluent neighborhoods).
- Predict store performance based on local purchasing power.
3. Competitive Benchmarking
Comparing store locations with competitors’ footprints highlights market gaps. Using data on chains like Walmart, Kroger, or Aldi, analysts can:
- Identify regions dominated by specific chains.
- Evaluate store performance based on proximity to competitors.
- Spot opportunities for niche markets, such as specialty grocers.
4. Predictive Modeling
Machine learning models, such as regression or clustering, forecast optimal locations. Features like population density, traffic patterns, and competitor presence predict store success. For example, a random forest model might rank potential sites based on projected revenue.
Table: Comparison of Grocery Store Location Data Sources
| Source |
Strengths |
Limitations |
Best Use Case |
| Government Databases |
High accuracy, verified data, free or low-cost |
Limited metadata, infrequent updates |
Baseline data for national analysis |
| Commercial Providers |
Comprehensive, rich metadata, frequent updates |
Costly, subscription-based |
Detailed market and competitive analysis |
| Web Scraping/APIs |
Real-time, customizable, includes customer reviews |
Requires technical expertise, potential legal restrictions |
Real-time updates, small-scale studies |
| Open-Source (e.g., OSM) |
Free, global coverage, community-driven |
Inconsistent quality, limited attributes |
Supplementary data, global or rural focus |
Significance of Grocery Store Locations Data
High-quality location data drives strategic decisions across the grocery retail ecosystem. Retailers use it to optimize site selection, reduce cannibalization, and target underserved markets. Grocery Delivery Scraping API Services provide granular insights into competitor store footprints and delivery zones, enabling more innovative expansion strategies. Investors leveraging insights rely on it to assess market potential and competition, while urban planners use it to improve food access, addressing issues like food deserts. Grocery Price Dashboard tools visualize pricing trends and store availability, which is crucial for evaluating affordability in low-income neighborhoods. Policymakers apply these insights to promote economic equity and public health. For example, analyzing store locations in low-income areas can inform subsidies for new stores, enhancing community access to fresh produce. Additionally, a Grocery Price Tracking Dashboard supports monitoring regional price changes, helping governments and retailers ensure transparency and responsiveness in food distribution strategies.
Conclusion
Extracting and analyzing top grocery store location data is a multifaceted process that combines rigorous methodologies, diverse data sources, and advanced analytical techniques. By sourcing accurate and comprehensive datasets from government records, commercial providers, APIs, and open-source platforms, stakeholders can build a solid foundation for analysis. Grocery Store Geolocation Data Scraping plays a vital role in collecting precise coordinates and store attributes across various regions. Geospatial, demographic, and predictive analyses transform raw data into actionable insights, guiding expansion, competition, and accessibility strategies. Businesses leveraging Grocery App Data Scraping Services gain deeper visibility into consumer behavior, delivery zones, and demand patterns. Additionally, Web Scraping Quick Commerce Data allows real-time monitoring of emerging retail trends and competitors in the rapid delivery segment. As the grocery retail landscape evolves, leveraging high-quality location data will remain critical for driving innovation and meeting consumer needs.
Are you in need of high-class scraping services? Food Data Scrape should be your first point of call. We are undoubtedly the best in Food Data Aggregator and Mobile Grocery App Scraping service and we render impeccable data insights and analytics for strategic decision-making. With a legacy of excellence as our backbone, we help companies become data-driven, fueling their development. Please take advantage of our tailored solutions that will add value to your business. Contact us today to unlock the value of your data.